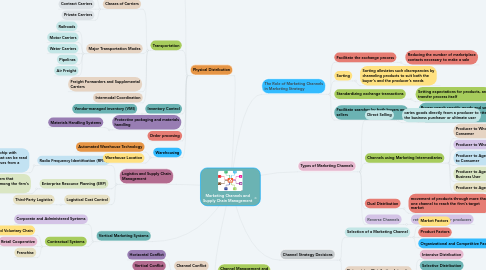
1. Channel Management and Leadership
1.1. Channel Conflict
1.1.1. Horizontal Conflict
1.1.2. Vertical Conflict
1.1.3. The Grey Market
1.2. Achieving Channel Cooperation
2. Vertical Marketing Systems
2.1. Corporate and Administered Syetems
2.2. Contractual Systems
2.2.1. Wholesaler-Sponsored Voluntary Chain
2.2.2. Retail Cooperative
2.2.3. Franchise
3. Logistics and Supply Chain Management
3.1. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)
3.1.1. technology that uses a tiny chip with identification information that can be read by a scanner using radio waves from a distance
3.2. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
3.2.1. integrated software system that consolidates data from among the firm's units
3.3. Logistical Cost Control
3.3.1. Third-Party Logistics
4. Physical Distribution
4.1. Customer service
4.2. Transportation
4.2.1. Classes of Carriers
4.2.1.1. Common Carriers
4.2.1.2. Contract Carriers
4.2.1.3. Private Carriers
4.2.2. Major Transportation Modes
4.2.2.1. Railroads
4.2.2.2. Motor Carriers
4.2.2.3. Water Carriers
4.2.2.4. Pipelines
4.2.2.5. Air Freight
4.2.3. Freight Forwarders and Supplemental Carriers
4.2.4. Intermodal Coordination
4.3. Inventory Control
4.3.1. Vendor-managed inventory (VMI)
4.4. Protective packaging and materials handling
4.4.1. Materials Handling Systems
4.5. Order procesing
4.6. Warehousing
4.6.1. Automated Warehouse Technology
4.6.2. Warehouse Location
5. The Role of Marketing Channels in Marketing Strategy
5.1. Facilitate the exchange process
5.1.1. Reducing the number of marketplace contacts necessary to make a sale
5.2. Sorting
5.2.1. Sorting alleviates such discrepancies by channeling products to suit both the buyer's and the producer's needs
5.3. Standardizing exchange transactions
5.3.1. Setting expectations for products, and transfer process itself
5.4. Facilitate searches by both buyers and sellers
5.4.1. Buyers search specific goods and services to fill theirs needs, while sellers attempt to learn what buyers want.
6. Types of Marketing Channels
6.1. Direct Selling
6.1.1. caries goods directly feom a producer to the business purchaser or ultimate user
6.2. Channels using Marketing Intermediaries
6.2.1. Producer to Wholesaler to Retailer to Consemer
6.2.2. Producer to Wholesaler to Business User
6.2.3. Producer to Agent to Wholesaler to Retailer to Consumer
6.2.4. Producer to Agent to Wholesaler to Business User
6.2.5. Producer to Agent to Business User
6.3. Dual Distribution
6.3.1. movement of products through more than one channel to reach the firm's target market
6.4. Reverse Channels
6.4.1. return goods to their producers
7. Channel Strategy Decisions
7.1. Selection of a Marketing Channel
7.1.1. Market Factors
7.1.2. Product Factors
7.1.3. Organizational and Competitive Factors
7.2. Determining Distribution Intensity
7.2.1. Intensive Distribution
7.2.2. Selective Distribution
7.2.3. Exclusive Distribution
7.2.4. Legal Problems of Exclusive Distribution
