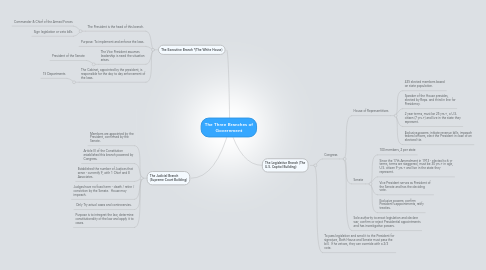
1. The Executive Branch *(The White House)
1.1. The President is the head of this branch.
1.1.1. Commander & Chief of the Armed Forces
1.1.2. Sign legislation or veto bills
1.2. Purpose: To implement and enforce the laws.
1.3. The Vice President assumes leadership is need the situation arises.
1.3.1. President of the Senate
1.4. The Cabinet, appointed by the president, is responsible for the day to day enforcement of the laws.
1.4.1. 15 Departments
2. The Judicial Branch (Supreme Court Building)
2.1. Members are appointed by the President, confirmed by the Senate.
2.2. Article III of the Constitution established this branch powered by Congress.
2.3. Established the number of Justices that serve - currently 9, with 1 Chief and 8 Associates.
2.4. Judges have no fixed term - death / retire / conviction by the Senate. House may impeach.
2.5. Only Try actual cases and controversies.
2.6. Purpose is to intrepret the law, determine constitutionality of the law and apply it to cases.
3. The Legislative Branch (The U.S. Capitol Building)
3.1. Congress
3.1.1. House of Representitives
3.1.1.1. 435 elected members based on state population.
3.1.1.2. Speaker of the House presides, elected by Reps. and third in line for Presidency.
3.1.1.3. 2 year terms, must be 25 yrs.+, a U.S. citizen (7 yrs.+) and live in the state they represent.
3.1.1.4. Exclusive powers: initiate revenue bills, impeach federal officers, elect the President in case of an electoral tie.
3.1.2. Senate
3.1.2.1. 100 members, 2 per state
3.1.2.2. Since the 17th Amendment in 1913 - elected to 6 yr terms, terms are staggered, must be 30 yrs.+ in age, U.S. citizen 9 yrs.+ and live in the state they represent.
3.1.2.3. Vice President serves as President of the Senate and has the deciding vote.
3.1.2.4. Exclusive powers: confirm President's appointments, ratify treaties.
3.1.3. Sole authority to enact legislation and declare war, confirm or reject Presidential appointments and has investigative powers.
