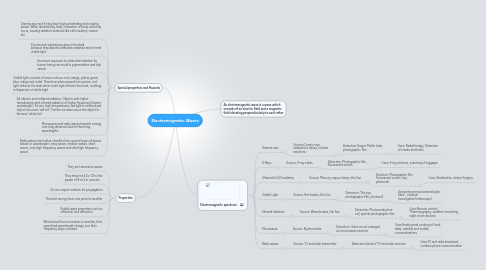
1. Properties
1.1. They are transverse waves
1.2. They travel at 3.0 x 10 to the power of 8 m/s in vacuum.
1.3. Do not require medium for propagation
1.4. Transmit energy from one point to another
1.5. Exhibit wave properties such as reflection and refraction
1.6. When travel from a medium to another, their speed and wavelength change, but their frequency stays constant
2. Special properties and Hazards
2.1. Gamma rays and X-rays have high penetrating and ionising power. When absorbed by body, ionisation of body cells may occur, causing radiation sickness like cell mutation, cancer etc.
2.2. Fluorescent substances glow in the dark because they absorb ultraviolet radiation and re-emit visible light.
2.3. Excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation by human being can result in pigmentation and skin cancer
2.4. Visible light consists of seven colours: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet. Therefore when passed into a prism, red light refracts the least while violet light refracts the most, resulting in dispersion of white light
2.5. All objects emit infrared radiation. Objects with higher temperature emit infrared radiation of higher frequency(shorter wavelength). At very high temperatures, red light is emitted and object becomes 'red hot'. Further increase cause the object to become 'white hot'.
2.6. Microwaves and radio waves transmit energy over long distances due to their long wavelengths
2.7. Radio waves are further classified into several types of waves based on wavelengths: long waves, medium waves, short waves, very high frequency waves and ultra high frequency waves
3. Electromagnetic spectrum
3.1. Gamma rays
3.1.1. Source:Cosmic rays, radioactive decay, nuclear reactions
3.1.1.1. Detection:Geiger-Muller tube, photographic film
3.1.1.1.1. Uses: Radiotherapy, Detection of cracks and faults
3.2. X-Rays
3.2.1. Source: X-ray tubes
3.2.1.1. Detection: Photographic film, fluorescent screen
3.2.1.1.1. Uses: X-ray pictures, scanning of luggages
3.3. Ultraviolet(UV) radiation
3.3.1. Source: Mercury vapour lamps, the Sun
3.3.1.1. Detction: Photographic film, fluorescent screen, dye, photocell
3.3.1.1.1. Uses: Sterilisation, detect forgery
3.4. Visible Light
3.4.1. Source: Hot bodies, the Sun
3.4.1.1. Detection: The eye, photographic film, photocell
3.4.1.1.1. Uses:telecommunications(optic fibre) , medical investigation(endoscope)
3.5. Infrared radiation
3.5.1. Source: Warm bodies, the Sun
3.5.1.1. Detection: Photoconductive cell, special photographic film
3.5.1.1.1. Uses:Remote control, Thermmography, weather forecating, night vision devices
3.6. Microwaves
3.6.1. Source: Klystron tube
3.6.1.1. Detection: Valve circuit arranged as a microwave receiver
3.6.1.1.1. Uses:Heating and cooking of food, radar, satellite and mobile communications
3.7. Radio waves
3.7.1. Source: TV and radio transmitter
3.7.1.1. Detection:Aerial of TV and radio receiver
3.7.1.1.1. Uses:TV and radio broadcast, cordless phone communication
